Radiology has deeply impacted dental medicine. This is no secret. Innovative institutions such as RIA Endovascular have led the way. With the rise of technology, our understanding of oral health has taken a great leap forward. We now see details we could not see before. We now treat conditions that were once untreatable. This is the power of radiology in dental medicine. Today, we explore this topic further. Remember, knowledge is the first step towards better health.
How Radiology Affects Dental Medicine
Radiology changes how we understand dental medicine. It allows us to see inside the teeth and jaw. We can detect early signs of disease. We can plan for surgeries. We can monitor the progress of treatment. Radiology does not just help diagnose. It guides treatment as well.
Types of Dental Radiology
There are many types of dental radiology. Each serves a specific purpose. Panoramic radiography gives us a broad view. It helps detect impacted teeth and jaw problems. Periapical radiography focuses on a single tooth. It shows us the tooth’s root and surrounding bone structure. Cone beam computed tomography (CBCT) provides a 3D image. It helps plan for implants and surgeries.
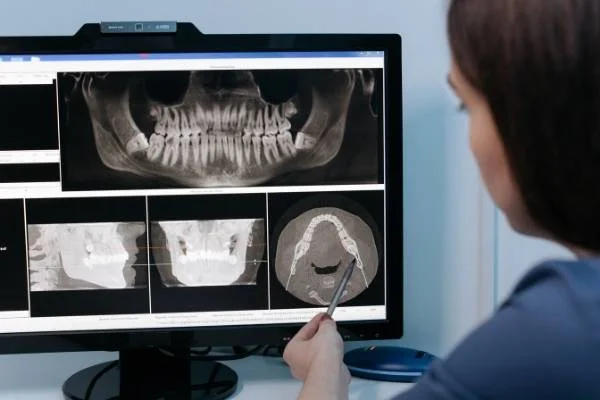
Table: Types of Dental Radiology and Their Uses
| Type of Radiology | Uses |
| Panoramic Radiography | Detects impacted teeth and jaw problems |
| Periapical Radiography | Shows a single tooth’s root and surrounding bone structure |
| Cone Beam Computed Tomography (CBCT) | Helps plan for implants and surgeries |
Is Dental Radiology Safe?
Yes, dental radiology is safe. The radiation dose is low. It is even lower than what we get from natural sources each day. A low dose does not mean no risk. But the benefits far outweigh the risks. Dental professionals take steps to minimize exposure. They use lead aprons and thyroid collars. They also use high-speed film to reduce exposure time.
Conclusion
Radiology has revolutionized dental medicine. It allows us to see what we could not see before. We can diagnose the disease early. We can guide treatment. We can monitor progress. It makes dental care more effective and less invasive.