It is highly recommended that a woman sees a gynecologist at least once per year. You could have questions about the menstrual cycle, birth control, impending or ongoing menopause, and infections. If you suspect having abnormal growth in the uterus or cervix, you need to see a gynecologist for thorough screening. A quick search for LEEP in Atlanta will lead you to a qualified team of specialists at Ideal Gynecology, LLC.
What is Cervical Cancer?
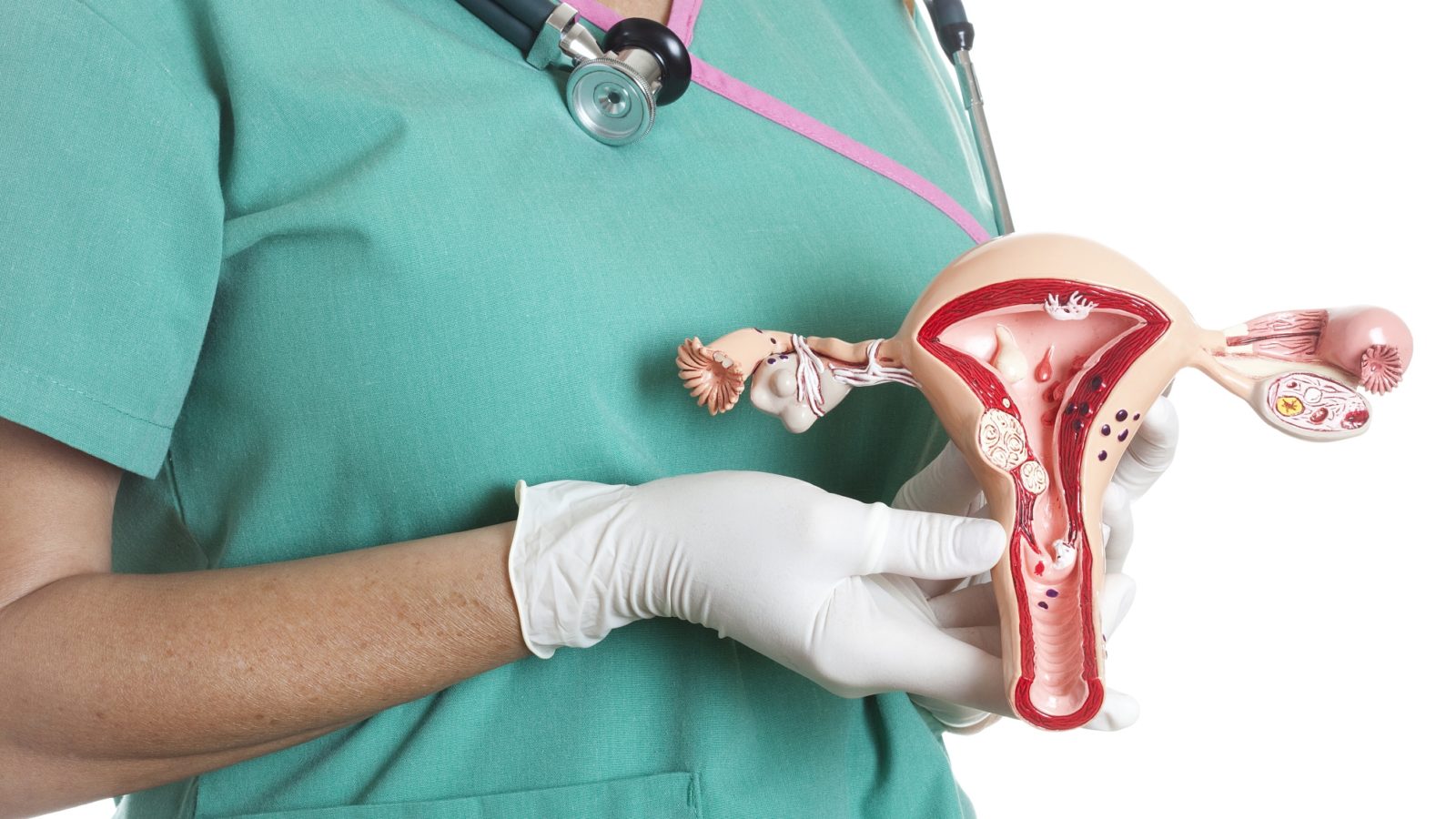
Cervical cancer is an unusual growth that occurs in the cervix of the uterus. The American Cancer Society estimates by the end of 2021, over 14,480 incidences of invasive cervical cancer will be diagnosed. Unfortunately, roughly 4,290 women succumb to the disease each year regardless of what treatment is offered.
Cervical cancer was once the foremost cause of death for women, but in the past four decades, the incidences and fatalities arising from this disease have declined sharply. More women are getting pap smear tests, and these efforts help in early detection and treatment, which saves lives.
Like many cancers, age is an essential factor that increases the risk of getting cervical cancer. Therefore, you must visit a gynecologist more often as you approach menopause and beyond. Symptoms of cervical cancer in the early stages include:
- Painful intercourse
- Unusual vaginal bleeding
- More vaginal discharge
- Bleeding after menopause
While just about any ethnicity can contract this disease, risk factors heighten the chances of getting cervical cancer. For example, people who have an HPV infection and those with multiple sexual partners stand a greater chance of getting abnormal growths in the cervix. HPV, in particular, is known to bring about cervical dysplasia, which is a precancerous problem claiming many lives.
Gynecologists recommend that women aged 21 – 65 get human papillomavirus testing so they can rule out HPV or detect it early enough. If you have young adults under your care, encourage them to get tested, and educate them about safe sex at all times.
Treatment of Cervical Cancer
Once you receive a positive test result, your doctor will need to determine how far the cancer is by performing imaging tests like MRIs, PET, and CT scans. A loop electrosurgical excision procedure (LEEP) eliminates malignant growth in the cervix. Other plausible treatment options include cryosurgery and laser surgery to remove abnormal growths. Starting treatment right away will bolster your chances of recovery, so your body is free of cancerous cells.
If you settle for LEEP, there are no special preparations needed; you only need to take painkillers similar to the ones you take to alleviate menstrual cramps. After the procedure, you may experience a bit of cramping and vaginal discharge for about two weeks. The fluid is thick initially but thins and lightens in a few days.
Cervical cancer still affects many women, and research shows that it impacts women in various demographics differently. Make it a priority to get a pap smear test before the year ends. Doing so will make it so you can either rest easy if all is well, or you can start treatment.