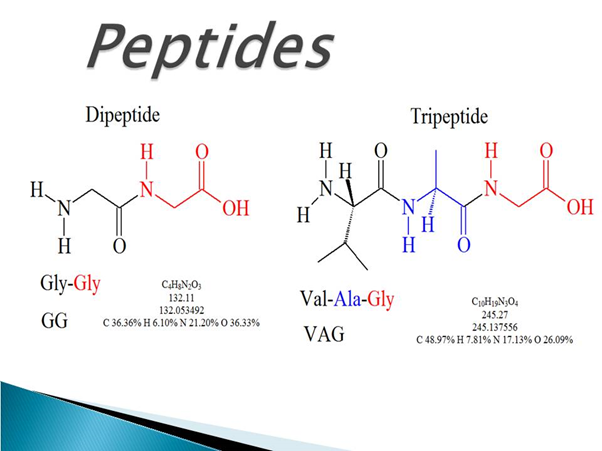
Peptides are chains of molecules known as amino acids, which are the basic components of proteins. Peptides are simply short proteins, typically containing between 2 and 100 amino acids.
Your body naturally produces peptides that play important roles in various processes. For example, insulin is a peptide hormone made up of 51 amino acids. It helps cells absorb sugars from food for energy and stores them in the liver.
Since 1921, researchers have been exploring peptides as potential treatments for different health conditions. Insulin was the first peptide to be created in a lab, and it has been used to treat people with type 1 diabetes since 1923.
Peptide medications might offer certain advantages over other types of drugs because they may:
- Be easier for your body to deliver to the right areas.
- Cause fewer side effects.
- Be safer, as your body breaks them down into amino acids, which it can reuse.
Some studies also suggest that peptides could benefit your skin, muscles, and even aid in weight loss. As a result, many companies have been adding them to skincare products and dietary supplements available over the counter and most turn to a Verified Peptides supplier.
Peptides vs. Proteins
Both peptides and proteins are made of amino acids connected by peptide bonds. The key difference is that peptides are shorter chains than proteins, although the terms are often used loosely. Generally, chains longer than 100 amino acids are considered proteins.
Peptides that contain about 10 to 20 amino acids are called oligopeptides, while chains with more than 20 amino acids are referred to as polypeptides.
Benefits of Peptides
Your body creates many different peptides, each with its own specific role. Synthetic peptides can also be produced in labs. For years, companies have been including peptides in skincare products. Some peptides may provide the following benefits:
Peptides for Anti-Aging
Collagen is a major protein in your skin, muscles, bones, tendons, ligaments, and other connective tissues. It helps these structures stay strong, flexible, and able to stretch. However, as you age, your body produces less collagen, and existing collagen breaks down faster, leading to wrinkles, sagging skin, and weaker muscles and bones.
Collagen injections can help smooth the skin and reduce wrinkles. Additionally, collagen supplements taken by mouth may keep your skin hydrated and elastic, especially for people over the age of 30. These supplements might also help with pain relief and improve joint function in people with osteoarthritis, a common form of arthritis caused by aging.
Your body cannot absorb collagen in its whole form, so it is often broken down into smaller peptides (called hydrolyzed collagen) for supplements. These supplements come in pill or powder form and can be found in health food stores, drugstores, and some grocery stores.
Copper peptides (GHK-Cu) are another type that may boost your body’s ability to produce collagen and elastin, a protein in the skin. Copper peptides are also antioxidants and assist with skin repair. Research shows that GHK-Cu in face creams may reduce wrinkles, age spots, and improve skin elasticity and thickness. It may also help promote hair growth. Copper peptides are available in various skin care products like lotions, creams, and serums. However, copper peptide injections were banned by the FDA in September 2023 due to safety concerns.
Another synthetic peptide called palmitoyl pentapeptide-4 (Matrixyl) might also enhance collagen production, improve skin texture, and reduce dark circles under the eyes. You can find Matrixyl in creams and serums available in stores where copper peptides are sold.
Peptides for Skin
Your skin naturally produces peptides, including antimicrobial peptides (AMPs), which help fight bacteria, heal wounds, and build a strong skin barrier. If your body produces too many or too few AMPs, it may result in skin conditions like psoriasis, eczema, rosacea, or acne.
Lotions and serums containing AMPs may help restore the skin barrier and reduce inflammation for people with psoriasis or eczema. These AMPs can also help prevent bacterial infections and may assist with healing skin ulcers, especially in people with diabetes. To use these products, you usually need a prescription, so consult your doctor if you’re interested.
Peptides for Muscle Growth and Weight Loss
Supplements like creatine and collagen may aid muscle growth or repair. Certain synthetic peptides called growth hormone secretagogues (GHS) may also be linked to muscle growth. However, these peptides may be unsafe and illegal in some cases. For example, they might interfere with your body’s insulin sensitivity and increase blood sugar. If you’re an athlete, note that all GHS peptides are banned by the World Anti-Doping Agency.
Peptides for Hair Growth
Certain peptides may help with hair growth, making it thicker and healthier. For instance, collagen peptides like GHK-Cu can stimulate hair growth in people with pattern hair loss. These peptides are available in serums you can apply to your scalp. Other options include collagen peptide supplements in pill or powder form, and folitin, another serum for scalp application.
Peptides for Bone Loss
Collagen peptide supplements can also help improve bone mineral density. In one study, people who took collagen peptide supplements daily for a year saw increased bone density in their upper back and upper leg bones, especially those assigned female at birth after menopause. Additionally, some peptide drugs are FDA-approved for treating osteoporosis.
Peptides for Testosterone
Some peptides may help raise testosterone levels by encouraging your body to produce and release hormones like gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH), luteinizing hormone (LH), and follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH). Two such peptides are kisspeptin-10 and gonadorelin. Studies show that kisspeptin-10 raised testosterone levels within 24 hours of injection, while gonadorelin helped restore testosterone levels and fertility in people assigned male at birth who had low testosterone due to inadequate GnRH production.
Peptide Therapy
Peptide therapy involves using peptides to improve certain body functions. For example, some athletes use growth hormone-releasing peptides to encourage the production of more growth hormone, which can aid recovery after intense exercise.
Peptides can be used in various forms:
- Oral supplements (pills or powders)
- Topical creams or patches
- Nasal sprays
- Injections (administered at a doctor’s office or wellness center)
Peptides are often injected because they are more effective when delivered directly into the bloodstream. Oral supplements may be less effective since the body breaks them down during digestion.
Peptide Supplements
Peptide supplements, such as pills or protein shakes, are available for various purposes like muscle building, recovery, and fat loss. However, there is limited evidence supporting most of these claims, and it’s unclear how well your body absorbs whole peptides from supplements.
Common peptide supplements include:
- Creatine peptide (promoted for muscle growth)
- Collagen peptide (promoted for skin, hair, and nail health)
- Follistatin (promoted for muscle gain and weight loss)
Peptides in Food
Peptides are naturally present in many foods, especially those rich in amino acids, such as:
- Meat
- Fish and shellfish
- Beans and lentils
- Soy
- Oats
- Flaxseed
- Hemp seeds
- Wheat
Peptide Drugs
Peptides are also used in medications for various conditions. Over 100 peptide drugs are FDA-approved in the U.S., including:
- Abarelix (for prostate cancer)
- Carfilzomib (for multiple myeloma)
- Enfuvirtide (for HIV)
- Exenatide (for type 2 diabetes)
- Linaclotide (for IBS)
- Teriparatide (for osteoporosis)
- Ziconotide (for severe chronic pain)
These drugs are thoroughly researched and tightly regulated by the FDA. Consult your doctor before taking any peptide drugs.
Side Effects of Peptides
Peptide therapy is generally safe when guided by a doctor. Most healthy people won’t experience serious side effects from peptide supplements. However, since supplements are not FDA-approved before sale, use caution when purchasing them, especially if you:
- Are pregnant or nursing
- Have a medical condition
- Are on medication
Possible side effects of peptide supplements include:
- Allergic reactions (hives, swelling, or difficulty breathing)
- Heart problems (high blood pressure, fast heart rate)
- Stomach issues (nausea, vomiting, diarrhea)
- Cognitive problems (headaches, dizziness)
- Skin reactions (rashes or sensitivity)
What You Should Know
Before trying any dietary supplements:
- Research the company’s website.
- Check the active ingredients.
- Be wary of unrealistic claims.
- Stick to the recommended dosage.
- Inform your doctor about any supplements you take, especially if you’re dealing with skin or hair issues.
If you experience an allergic reaction to a peptide-based product, seek medical help immediately.
Takeaways
Peptides are short protein chains made up of 2 to 100 amino acids. Your body produces peptides that play essential roles in digestion, energy use, hunger regulation, and hormone function. Peptides have been used in medicines for over 100 years and are included in supplements and skincare products for anti-aging, muscle growth, and fat loss benefits.
Peptides FAQs
Are peptides steroids?
No, peptides and steroids are different. Peptides are chains of amino acids, while steroids are ring-shaped fatty molecules. Although both can help build muscle and burn fat, they work through different processes. Steroids have more severe side effects and are regulated, while peptides are more widely available.
What are the side effects of peptides?
Side effects vary depending on the peptide used, but most are considered safe when taken properly. Some peptides have not been thoroughly tested, so it’s essential to be cautious.