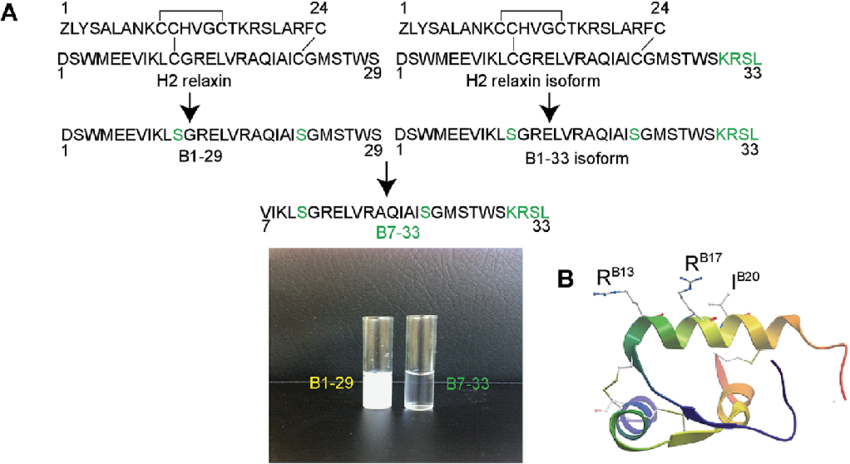
B7-33 is a water-soluble single-chain peptide derived from the naturally occurring larger protein H2-relaxin. B7-33 retains all the anti-fibrotic properties of relaxing without increasing cAMP production. By phosphorylating ERK1/2, this peptide increases the formation of matrix metalloproteinase 2 and the breakdown of extracellular collagen.
The human H2-relaxin protein is the flagship of the family of relaxin protein 4 proteins, and B7-33 is one of the numerous synthetic peptides derived from it. You can now buy B7-33 peptide online.
Pleiotropic effects have been discovered in all of these very closely related proteins, impacting the cardiovascular system, musculoskeletal system, and reproduction. B7-33 for sale is in high demand, thus it is easy to find it on the internet.
Endogenous relaxin family peptide receptors are divided into two groups (RXFP1/2 and RXFP3/4). Here is the list of these receptors’ functions:
- Sperm motility, pregnancy, the endothelium of the blood vessels, and joint health all are vital.
- Has a considerable effect on testicular degeneration.
- Mutations in this receptor have been associated with various sleep disorders and schizotypal personality disorder.
- This receptor’s function is less defined. It has been shown to have an effect on insulin-like peptide 5 that has been shown to play a function in hunger signaling and is expressed on sperm.
Orexin, CAMP, corticotropin-releasing factor (CRF), numerous insulin-like peptides, and GLP-1 all trigger relaxin receptors. Anti-inflammatory, antioxidants, and wound-healing capabilities are all present in these agonists.
Relaxin can possess all the qualities except vasodilator, antihypertrophic, and blood vessel growth stimulant according to research. As a result, the peptide and all its derivatives can be employed to treat acute heart failure as well as other fibrotic diseases.
Latest SANOFI Patents
- A device for data collection to an injection
- A medication delivery device’s audible indicator
- Device for delivering drugs
Peptide Working Mechanism
Aside from the structural differences, the peptide differs from endogenous proteins in a number of ways that are more advantageous than H2-relaxin itself.
Instead of using the cAMP pathway, the B7-33 peptide uses the pERK pathway. H2-relaxin’s anti-fibrotic activities are typically attributed to the cAMP pathway, which has the potential to promote the growth of tumors in our body. This is a significant side effect of relaxin therapy.
In addition, the peptide exhibits a high affinity for RXFP-1 receptors. The peptide binds to these RXFP-1 receptors and activates the pERK pathway, resulting in enhanced MMP-2 matrix metalloproteinase chemical production. These substances then prevent fibrosis by preventing scarring of the tissues.
Biological Applications of B7-33 Peptide
In the field of human medicine, this peptide has showed a number of benefits, including:
- Antifibrotic characteristics are present in this substance.
- Blood vessel protection capability
- Aids in the treatment of preeclampsia.
- Use as a body implant covering material
Research and Clinical Studies
H2 relaxin was known to be a strong vasoprotective drug, owing to its favorable effects in heart failure treatment and fibrosis.
Due to the high cost and time involved in synthesizing H2 relaxin exogenously, it turned out to be more vital to investigate and determine whether its counterpart B7-33 peptide had similar effects.
The tails of male wistar rats were injected with either a placebo, H2 relaxin, or B7-33 in this 2017 study.
These mice were tested for vascular functions, primarily in the renal artery, mesenteric artery, and abdominal aorta, three hours after being given the drug.
While the results in the renal artery and abdominal aorta were not too promising, both H2 relaxin and B7-33 demonstrated increased vasodilatory characteristics in the mesenteric artery.
These findings show that B7-33 can mimic H2 relaxin’s vasoprotective properties and so protect blood vessels from any further injury. The findings also suggest that the peptide could be used to treat some cardiovascular diseases.